New Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) Compares Carbon Emissions of NMC 622 Cathode Material Made with Mined Metals Vs. NMC 622 Hydro-to-Cathode® Battery Materials Made with Recycled Materials
WESTBOROUGH, Mass., (January 30, 2024) — Using its patented Hydro-to-Cathode® process and recycled materials, Ascend Elements can today manufacture new EV battery material (NMC 622 cathode) at a 49% reduction in carbon emissions compared to traditional cathode manufacturing processes that rely on primary materials from mining. By 2030, the company aims to achieve a 90% reduction in carbon footprint for its NMC 622 cathode product, according to a new Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) published this week. The study was conducted by a third-party in accordance with the ISO 14067:2018 standard and independently reviewed and verified.
“We have an opportunity to make new EV battery materials, and new EVs, far cleaner than they are today,” said Mike O’Kronley, CEO of Ascend Elements. “With our ultra-efficient Hydro-to-Cathode® process and use of recycled battery materials instead of primary materials from mining, we can cut the climate impact of new cathode material in half. Beyond that, we’re on a path to achieve a 90% reduction in carbon footprint by 2030.”
The company’s decarbonization path includes use of 100% renewable energy in its recycling and manufacturing facilities, use of rail to transport materials, and use of responsibly sourced lithium carbonate (Li²CO³).
According to the study, the production of 1 kg of typical cathode material (NMC 622 with primary material from mining) generates 42.8 kg of CO2 emissions. Using Ascend Elements’ manufacturing process today with recycled battery material, the production of 1 kg of NMC 622 cathode generates 21.9 kg of CO2 emissions. With the company’s decarbonization plans achieved by 2030, the production of 1 kg of NMC 622 cathode will generate just 4.4 kg of CO2 emissions.
“To put these numbers in perspective, if we manufacture 10,000 metric tons of Hydro-to-Cathode® NMC 622 using our decarbonized future process, the carbon emissions reduction would be like removing 83,500 gas-powered cars from the road for one year.”
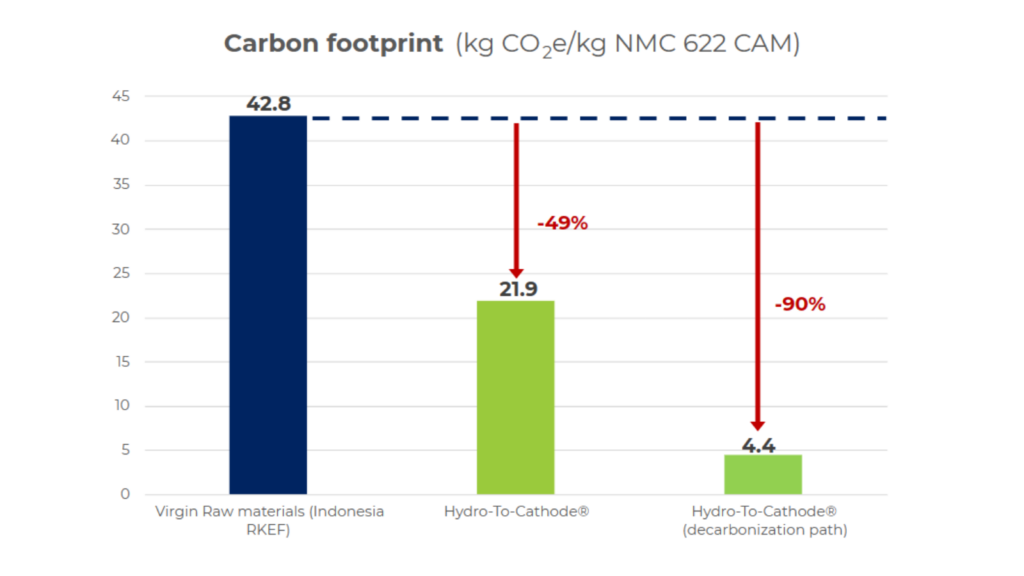
A summary of the LCA Study is available for download. Carbon emissions for “typical cathode” are based on the use of nickel sulfate hexahydrate from Indonesian laterites using nickel matte via RKEF as an intermediate; cobalt sulfate from ore mined in the DRC and refined in China; and manganese sulfate mined in South Africa and refined in China.
Founded in 2015 and based in Massachusetts, Ascend Elements is a leading provider of sustainable, closed-loop battery material solutions. From EV battery recycling to commercial-scale production of lithium-ion battery precursor (pCAM) and cathode active materials (CAM), Ascend Elements is revolutionizing the production of sustainable lithium-ion battery materials. Its Hydro-to-Cathode® direct precursor synthesis technology produces new CAM from spent lithium-ion cells more efficiently than traditional methods, resulting in improved economics and lowered GHG emissions. With fewer batteries going to landfill and a cleaner manufacturing process, Ascend Elements is taking the lithium-ion battery industry to a higher level of sustainability.
MEDIA CONTACT:
Thomas Frey, APR
Ascend Elements | [email protected] | +1.734.658.0143

